Bot Fly Larva
The parasitic fly is an insect that can be found all over the world. Most of them are found in Central and Southern Africa. There are many types, such as the horse fly, the deer fly, but the most frightening is the human fly. This parasitic fly will lay eggs on mosquitoes or any insects that often fly and land on people. When the mosquito sucks human blood, the eggs of the parasitic fly will move to the skin. Then, when it grows from a pupa and becomes a larvae under the skin, it will then eat the sap and some of the tissue of our skin. On a good day, it may crawl to eat various organs in our body, such as the brain, eyeballs, testicles. When it is fully grown, it will push itself out, like an alien emerging from the body.

Myiasis
A condition in which maggots live in humans or living animals for a period of time. These maggots may suck the host’s tissue, fluids, or food that the host has eaten.
There are two ways to classify myiasis:
1. Clinical classification
2. Parasitological classification
1. Clinical classification
This method is classified based on the location where the maggots live in the host. This classification makes it easier to classify maggots. It can be divided into:
# Cutaneous myiasis
This is a myiasis that occurs on the skin or under the skin, such as maggots, when maggots crawl up the host and suck blood (Bloodsucking myiasis), a condition in which maggots burrow into the skin and form a boil (Furunicular myiasis), or when maggots burrow along the skin, forming a line where they burrow (Creeping myiasis), or some maggots that like to live in the host’s wounds (Wound or Traumatic myiasis).
Body cavity myiasis is myiasis that occurs in various cavities of the host body, such as nasophalyngeal myiasis, auricular myiasis, ophthalmomyiases
in the mouth

Myiasis occurring in various internal organs
such as in the digestive tract (Enteric or Intestinal myiasis), myiasis occurring in the bladder (Urogenital myiasis) or in the female reproductive organs (Vaginal myiasis).

Myiasis occurring in various internal organs
such as in the digestive tract (Enteric or Intestinal myiasis), myiasis occurring in the bladder (Urogenital myiasis) or in the female reproductive organs (Vaginal myiasis).

2. Parasitological classification
Based on the relationship between the host and the maggot, this classification allows us to better understand the biology of flies. It also provides a guideline for disease treatment and prevention, and also helps us to better understand the evolution of maggots. This classification of myiasis can be divided into 3 groups:
Specific or Obligatory myiasis is a type of myiasis in which the maggot must live on the host throughout its larval stage, for example, the maggot Chrysomya bezziana must grow only in the wound of the animal.
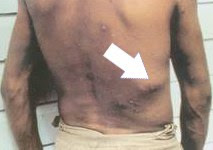
Skin myiasis (arrow)
Semi-specific myiasis or
semi-obligatory myiasis or
facultative myiasis is a myiasis in which the maggot lives on the host only for part of its life cycle. For example, the maggot Auchmermyia hiteola (congo floor maggot) in Africa, which lives on the ground around houses, will come to suck blood while people are sleeping, then drop back to the ground.
Oh, it’s like Dracula, coming while sleeping. Hehe
Auchmermyia hiteola (congo floor maggot) larvae sucking blood
Bedbugs
They are like small ticks that live around our sleeping area. They usually come out to feed at night, but sometimes they can come out during the day. Because of their small size, they can hide inside the mattress, in the seams of the mattress, in the carpet, in cracks in the wall, under underwear, holes in underwear, and almost anywhere in the bedroom. It’s possible that they might even gather in underwear. Bedbugs can walk 100 feet looking for blood.
Their bites are often confused with mosquitoes or spiders because their bites are both itchy and red. Fortunately, there is no information that bedbugs are carriers of diseases. However, they can cause infection if you scratch until you get a wound. However, if we find out too late that what bit us is a bedbug, not a mosquito, the bedbugs will have a greater chance of breeding.
The main problem with bedbugs is not that they itch when bitten, but because of psychological symptoms. Most of the time, as soon as a bedbug is found in the room, the host [or the person who is used by the parasite as a shelter] will often experience severe anxiety and fear because bedbugs do not come alone. But not much….look at the picture = =’
Not only that, bedbugs are very difficult to detect because of their ability to hide. Wherever an insect the size of an apple seed can get in, bedbugs can get in. It might even get into our noses. Haha!! Just kidding. They can survive for a year without eating. The real scariest thing about them is that females can lay more than 500 eggs in their lifetime and will start sucking blood from the moment they hatch. It takes only 5 weeks to become fully grown and ready to lay eggs!! Come on!!
Lice
Actually, there are many types of this insect, but the most well-known seems to be head lice. But there are also body lice, also called lice. What’s scary is that there are lice in secret areas. From what I’ve said, they all thirst for human blood. In fact, there are many other species, but they only infect animals.
The lifespan of lice is quite short. Eggs hatch in 6-9 days, become larvae, and molt 3 times before reaching maturity. Fragments of eggs and lice residue are left behind, like when the author takes off his shirt and throws it away without folding it. Adults move very quickly and live for about a month to feed on blood and reproduce. Females can lay about 7-12 eggs per day.
Lice are much easier to detect than bedbugs. You can tell by the itching and red rash in the area where they live, but sometimes there may be bumps where they were bitten. Just a good comb with many teeth or a lice comb can remove both lice and eggs. However, medication is more certain. You should also check the heads of other people in the house to see if they are infected.
Leeches
Most blood-sucking leeches are found in still or slow-flowing water, but they can also be found on land. Their way of finding their host is to wait on the bottom of the water and take their time to detect movement or light changes its shape. When they find their host, they will wave and ‘swim’ to find their host.
Leeches use the sucking parts of their mouthparts and many teeth to create wounds on their hosts. After that, the leech will secrete a mucus-like substance [Eww, did I get told to snot!?] to keep their bodies attached to their hosts. The leech will relax after releasing its antifreeze and digestive juices. In order to prevent the blood from clotting or becoming indigestible, this is a property of leeches that can be used in medicine.
Leech wounds are not as bad as many people think. They may be annoying and ooze liquid blood for several hours, but only a small amount of blood is lost. Infections are rare and allergic reactions are not a big concern.
Mites
Mites are one of the most common creatures, but there are so many types, such as dust mites, bird mites, dog mites, deer mites, and scabies mites. There are even mites that are currently living on our bodies, and they are feeding on the oils on everyone’s heads. So, we don’t really need to wash our hair. Oops! No way!! But don’t worry, these mites are normal and harmless. Most mites don’t cause much trouble to people, but they will feed on blood instead if their original food supply is gone. It’s like they are dissatisfied and use blood to protest. Hey! Sounds familiar, never mind.
The mite that often causes problems for people is the scabies mite. This tiny parasite can cause extreme itching and red rashes on the infected area. This type of infection is diagnosed as parasitic dermatitis and is treated with medication prescribed by the doctor.
Tapeworms
Tapeworms are similar to hookworms in that they are intestinal parasites that can be transmitted through soil or waste. However, they are mostly transmitted through humans eating undercooked food, which makes it impossible to kill the parasites. [Oh, that’s what the health teacher tried to warn us about many times.] These parasites live in the muscles of animals after they have been eaten along with lush green grass, and humans end up killing the animals to feed us.
When an unfortunate person eats tapeworm eggs, the eggs hatch during digestion and grow from larvae to adults, feeding on blood and nutrients in the small intestine. The adults are either male or female, or even transvestites. They can produce eggs and release them in human waste, like using feces as a vehicle. 55+ The eggs that are released may get stuck in the toilet bowl, or they may flow down the drain to a new place and start the life cycle again.
Symptoms of tapeworms are very difficult to recognize because there are no external symptoms for a long time. And it can make this cute tapeworm grow to be 30 feet long. But as it grows, it may also show symptoms of a bloated belly. But if you don’t know you have a tapeworm, these guys can grow big and live for decades.
Hookworms [Worms